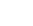
Effect of Smartphone-Based Telemonitored Exercise Rehabilitation among Patients with Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract:The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of telemonitored exercise rehabilitation on patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) in China. Ninety-six patients with stable CHD were included and analyzed (48 in telemonitored group and 48 in control group). All patients received routine follow-up, and patients in telemonitored group participated in smartphone-based telemonitored cardiac rehabilitation. Patients' demographic information, medical history, diagnosis and treatment of CHD, and laboratory results were collected. The difference of cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET), blood test, and echocardiographic parameters; exercise habits; control rate of blood lipid and blood glucose; and incidence of adverse events between the two groups during 6 months of follow-up was analyzed. After intervention, the subjects in the telemonitored group performed significantly better in VO2peak, exercise compliance, and some other parameters than those in the control group. Telemonitored exercise rehabilitation is an effective rehabilitation mode for CHD patients in China.
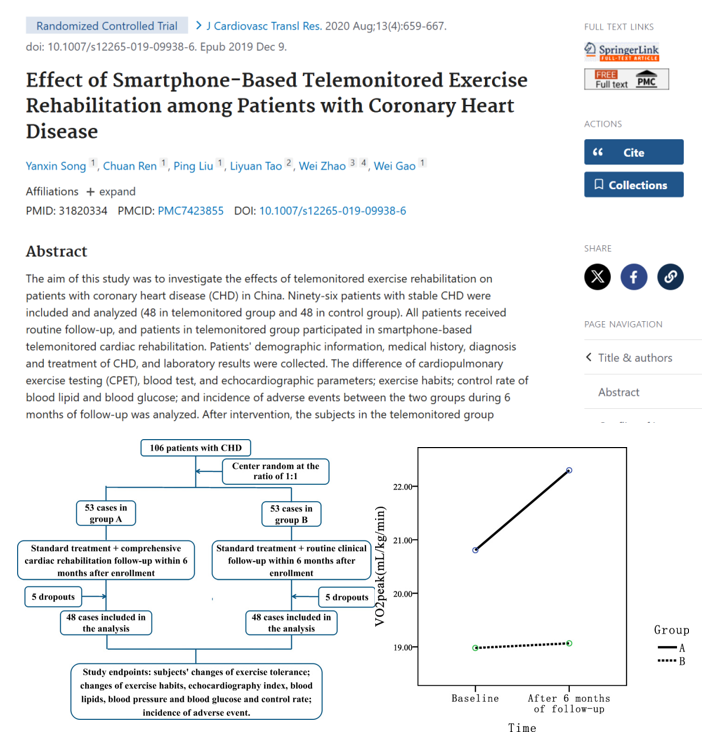
Gut microbiota combined with metabolites reveals unique features of acute myocardial infarction patients different from stable coronary artery disease
Introduction: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) accounts for the majority of deaths caused by coronary artery disease (CAD). Early warning of AMI, especially for patients with stable coronary artery disease (sCAD), is urgently needed. Our previous study showed that alterations in the gut microbiota were correlated with CAD severity.
Conclusion: Combination of gut microbiota and fecal/urinary metabolites provided a set of potential useful and noninvasive predictive biomarker for AMI from sCAD.
Waistline to thigh circumference ratio as a predictor of MAFLD: a health care worker study with 2-year follow-up
Background: This study aimed to determine whether the waist-to-thigh ratio (WTTR) is associated with the incidence of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in health care workers.
Conclusions: Our results revealed that the WTTR is an independent risk factor for MAFLD, and there was a dose‒response relationship between the WTTR and MAFLD risk. The neck circumference was significantly different in subjects with a BMI < 23 kg/m2. This approach provides a new way to predict the incidence rate of MAFLD.
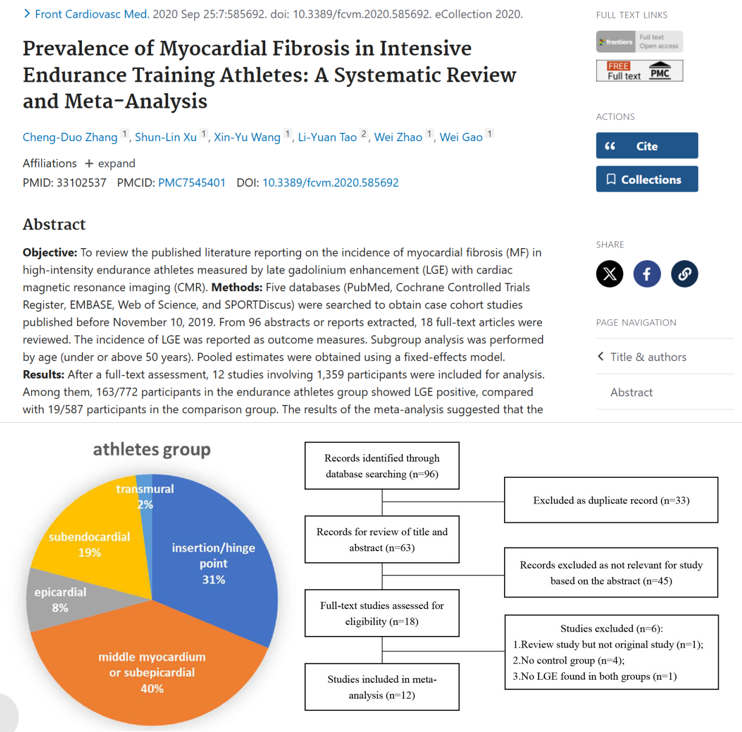
Prevalence of Myocardial Fibrosis in Intensive Endurance Training Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Objective: To review the published literature reporting on the incidence of myocardial fibrosis (MF) in high-intensity endurance athletes measured by late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR).
Conclusions: The available evidence demonstrates that high-intensity endurance athletes is associated with an increased incidence of LGE positive.