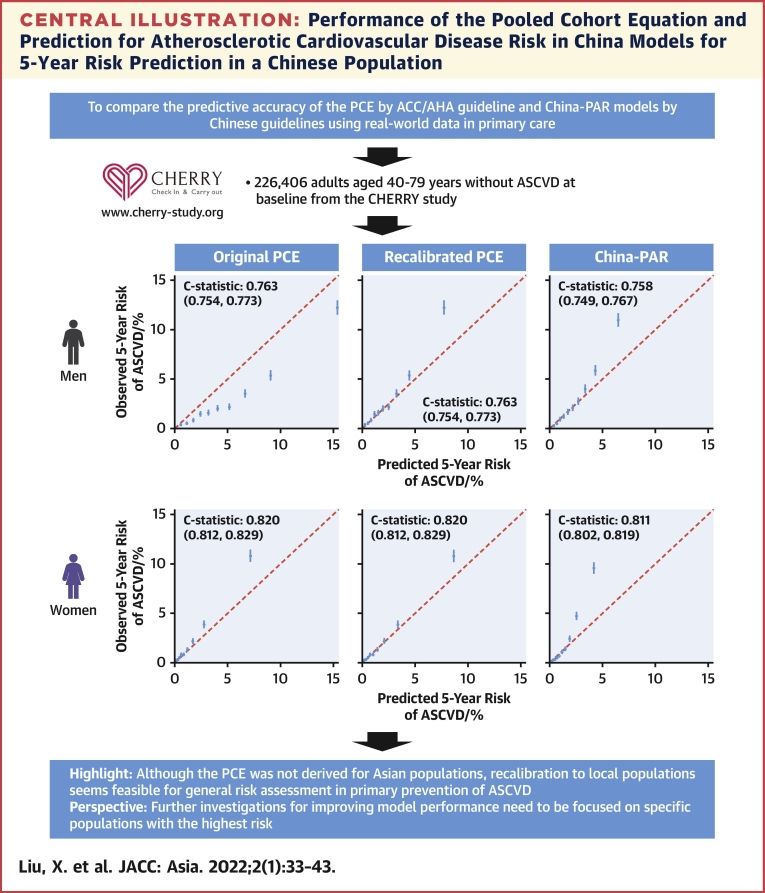
Evaluation of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk Prediction Models in China: Results From the CHERRY Study
Objectives: The authors aimed to evaluate the accuracy of the PCE or China-PAR models in a Chinese contemporary cohort.
Conclusions: In this large-scale population-based study, both PCE and China-PAR had good discrimination in 5-year ASCVD risk prediction. China-PAR outperformed PCE in calibration, whereas recalibration equalized the performance of PCE and China-PAR. Further specific models are needed to improve accuracy in the highest-risk groups.

Rationale, design and population description of the CREDENCE study: cardiovascular risk equations for diabetes patients from New Zealand and Chinese electronic health records
Abstract:The cardiovascular risk equations for diabetes patients from New Zealand and Chinese electronic health records (CREDENCE) study is a unique prospectively designed investigation of cardiovascular risk in two large contemporary cohorts of people with type 2 diabetes from New Zealand (NZ) and China. The study was designed to derive equivalent cardiovascular risk prediction equations in a developed and a developing country, using the same epidemiological and statistical methodology.

Validation and comparison of cardiovascular risk prediction equations in Chinese patients with Type 2 diabetes
Aims: For patients with diabetes, the European guidelines updated the cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk prediction recommendations using diabetes-specific models with age-specific cut-offs, whereas American guidelines still advise models derived from the general population. We aimed to compare the performance of four cardiovascular risk models in diabetes populations.
Conclusion: Diabetes-specific CVD risk prediction models showed better discrimination for patients with diabetes. High-risk patients selected by different models varied significantly. Age-specific cut-offs selected fewer patients at high CVD risk especially in women.

Prevalence and Incidence of Heart Failure Among Urban Patients in China: A National Population-Based Analysis
Background: Large-scale and population-based studies of heart failure (HF) incidence and prevalence are scarce in China. The study sought to estimate the prevalence, incidence, and cost of HF in China.
Conclusions: HF has placed a considerable burden on health systems in China, and strategies aimed at the prevention and treatment of HF are needed. Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: ChiCTR2000029094.

Incidence and Survival of Aortic Dissection in Urban China: Results from the National Insurance Claims for Epidemiological Research (NICER) Study
Background: Aortic dissection (AD) represents a significant mortality; however, there is rare epidemiologic information about the demography of AD in Chinese, especially its incidence rate.
Findings: 6084 adult AD cases were included in incidence analysis. Totally 4692(77.1%) were men and 5641(92.7%) were Han Chinese. The overall age- and sex-adjusted incidence rate of AD was 2.78(95%CI:2.59-2.98) per 100,000 person-years. In terms of geographic disparities, the crude incidence rate was significantly higher in Northwest China than South China (4.96[95%CI:4.17-5.75] vs. 2.04[95%CI:0.38-3.71] per 100,000 person-years; risk ratio: 2.67[95%CI: 2.34-3.04]). Moreover, survival analysis of 4518 AD patients with 683 recorded deaths during follow-up (median 2.2 years) showed that overall 3-year survival was 83.7%(95%CI:82.4-84.8).
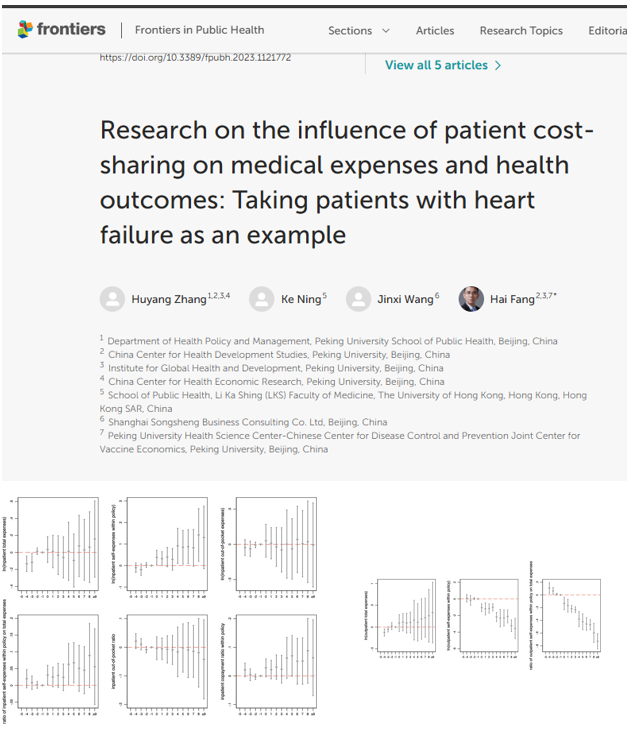
Research on the influence of patient cost-sharing on medical expenses and health outcomes: Taking patients with heart failure as an example
Objective: The objective of this study is to assess the impact of the changes in patient cost-sharing on the medical expenses and health outcomes of patients with heart failure in China.
Conclusion: The impact of the policy change on medical expenses and health outcomes was found to be modest. To effectively address the financial burden on patients, it is crucial for policymakers to adopt a comprehensive approach that considers all aspects of medical insurance policies, including reimbursement policies.